When we say “distance”, what do you think about? The distance between your home and your workplace? What is the shortest distance to arrive somewhere? In this blog, I will talk about how we apply distance in Data Science with the following points:
- Haversine distance
- Real distance
- Use cases
Haversine distance
What is Haversine distance?
Here, Haversine distance also means great-circle distance, which is the shortest distance between two points on the surface of a sphere, measured along the surface of the sphere (as opposed to a straight line through the sphere’s interior). The distance between two points in Euclidean space is the length of a straight line between them, but on the sphere there are no straight lines. In spaces with curvature, straight lines are replaced by geodesics. Geodesics on the sphere are circles on the sphere whose centers coincide with the center of the sphere, and are called great circles.
How to calculate Haversine distance in math?
An illustration of the central angle, Δσ, between two points, P and Q. λ and φ are the longitudinal and latitudinal angles of P respectively.
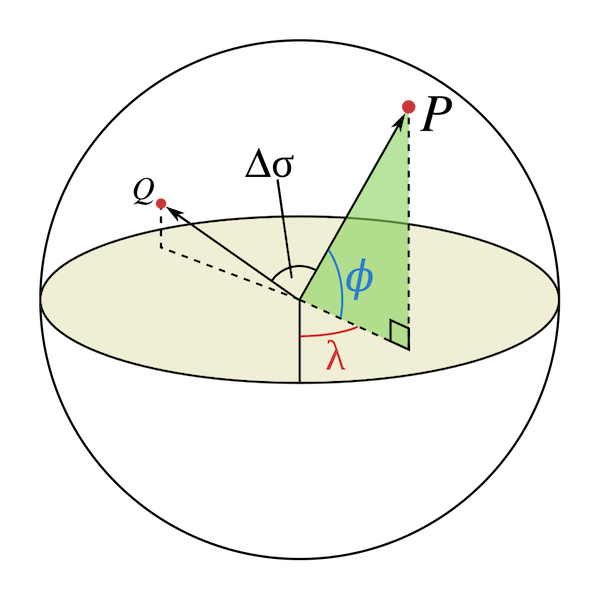
Let ,
and
,
be the geographical longitude and latitude in radians of two points 1 and 2,
and Δλ, Δφ be their absolute differences; then Δσ, the central angle
between them, is given by the spherical law of cosines if one of the poles is
used as an auxiliary third point on the sphere:
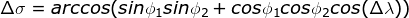
How to calculate Haversine distance in Data Science?
Before running, we need to install haversine module.
>>> from haversine import haversine
>>> haversine((48.856614, 2.3522219), (43.60426, 1.44367))
588.1899001977165 # Haversine distance between Paris and ToulouseReal distance
What is Google Distance Matrix API?
For the real distance between two locations, I usually use the Google Distance Matrix API, which is a service that provides travel distance and time for a matrix of origins and destinations, based on the recommended route between start and end points.
We access the Distance Matrix API through an HTTP interface, with requests constructed as a URL string, using origins and destinations, along with your API key. The following example requests the distance matrix data between Washington, DC and New York City, NY, in JSON format:
https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/distancematrix/json?units=imperial&origins=Washington,DC&destinations=New+York+City,NY&key=YOUR_API_KEYHow to use Google Distance Matrix API in Data Science?
I saved my Google Distance Matrix API key in a .properties file, named as
“key.properties” in advance. Then I created a function
get_itinerary(origin_lat, origin_lng, dest_lat, dest_lng) to get distance
and duration between 2 locations.
import configparser
from urllib.parse import urlencode
import requests
def get_itinerary(origin_lat, origin_lng, dest_lat, dest_lng):
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('key.properties')
key = config['google']['data.science']
origin = '%f, %f' % (origin_lat, origin_lng)
destination = '%f, %f' % (dest_lat, dest_lng)
response = requests.get(
'https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/distancematrix/json?language=en&' +
urlencode({'origins': origin,
'destinations': destination,
'mode': 'driving',
'key': key}))
distance_info = response.json()
try:
if distance_info['rows'][0]['elements'][0]['status'] == 'OK':
duration = distance_info['rows'][0]['elements'][0]['duration'][
'value'] / 60
distance = distance_info['rows'][0]['elements'][0]['distance'][
'value'] / 1000
return [duration, distance]
else:
return ['', '']
except IndexError:
print('Failed to get status, response:', distance_info)
raiseIn this example, I choose driving mode with 'mode': 'driving', you can modify
the mode as you need.
Use cases
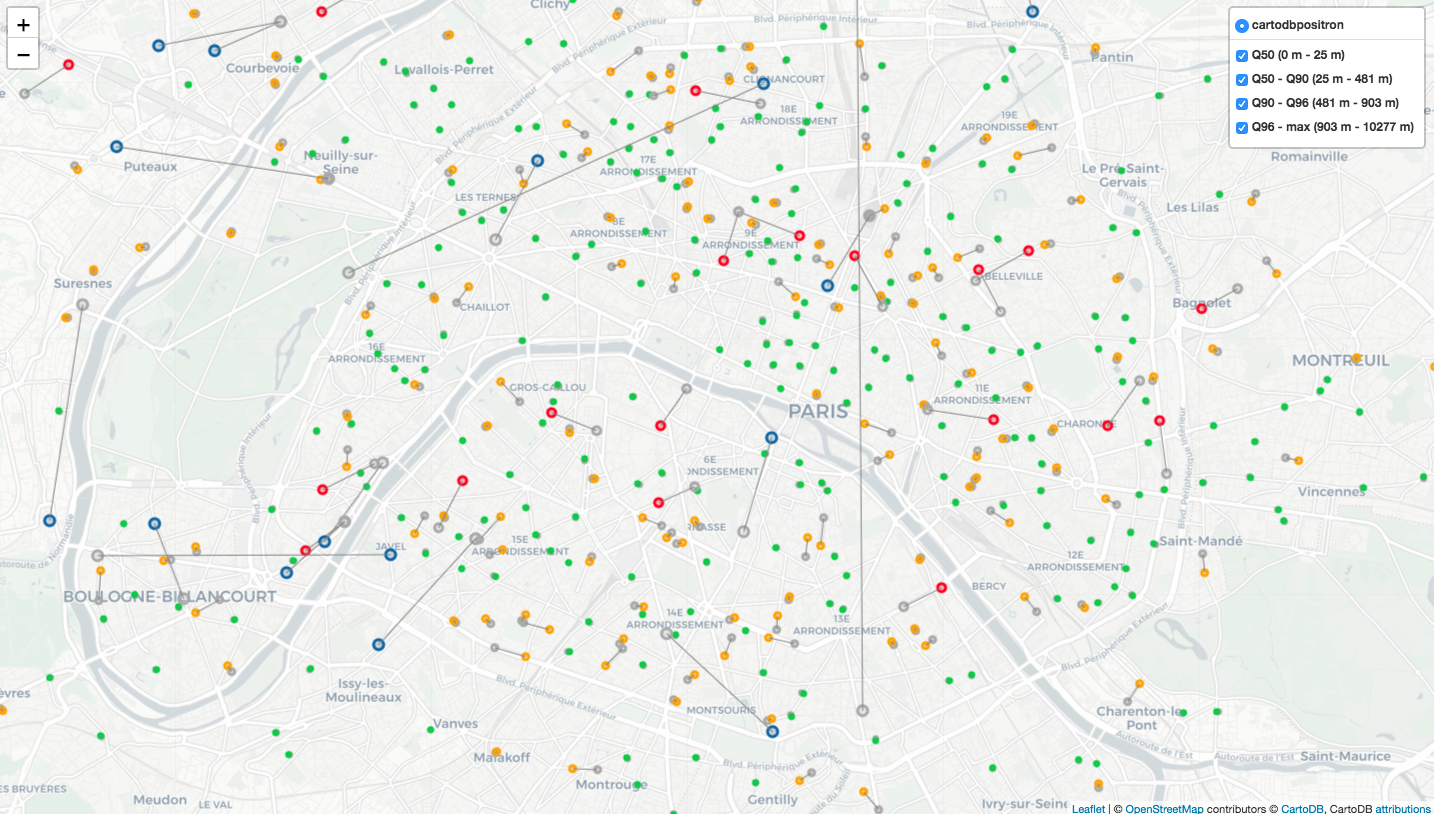
Stores geolocation
We have latitude and longitude for each store in our internal system, but some are not that exact, so we decide to check and update geolocation’s information for each store, and specify the haversine distance between geolocation of internal system and new defined geolocation.
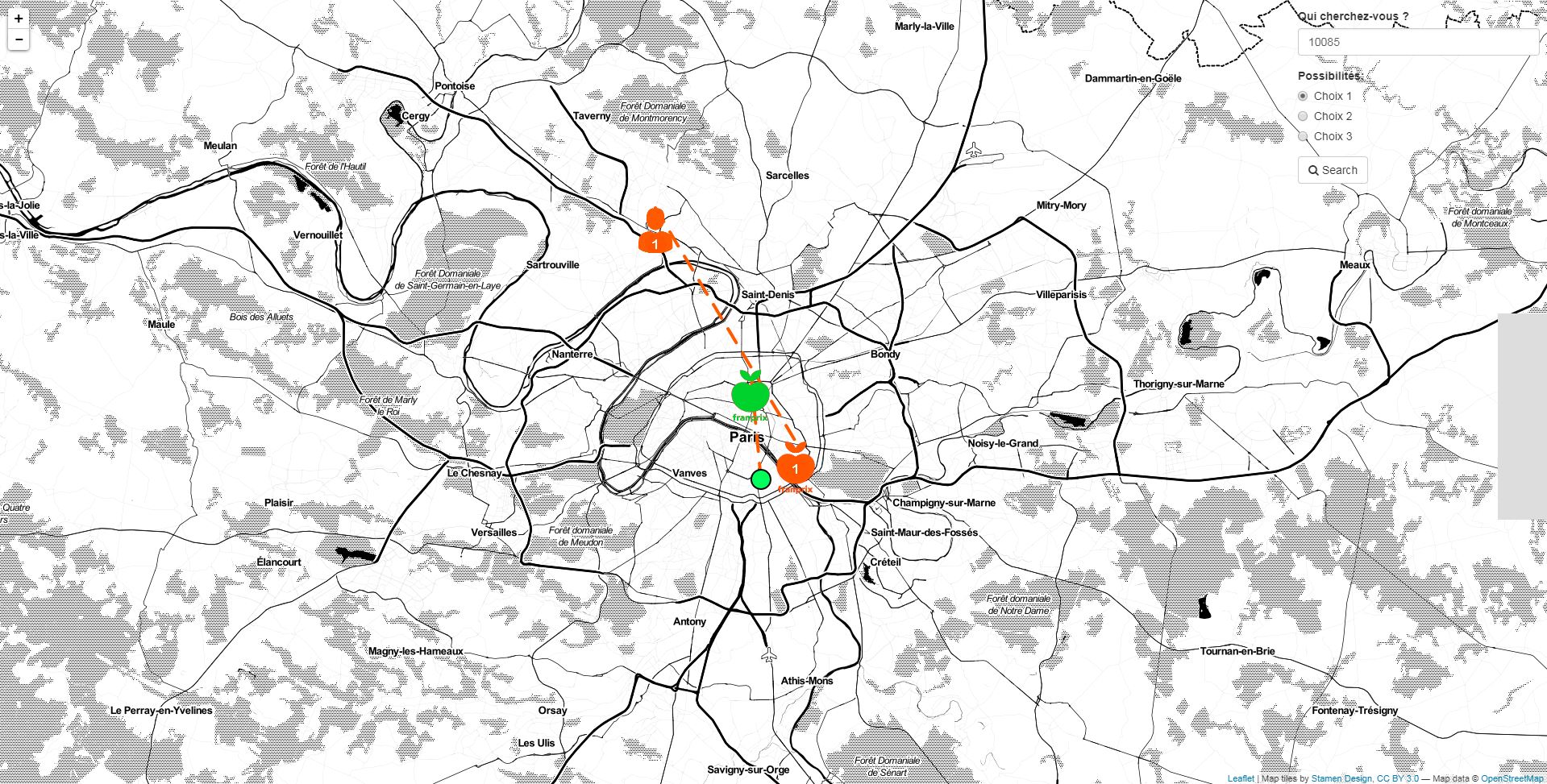
Exchange of employees’ workplaces
As enterprise growing, there are more and more shops spread all over France, so are its employees. Some employees take such a long duration for working and going home. To facilitate the way between one’s home and workplace, CEO proposed that 2 employees can exchange their workplaces, if it saves time for both. This project is for finding the optimal solution for all employees. We applied Google Distance Matrix API, created a tool for visualising and simplifying the employee-switching. As the graph below, we can enter an employee ID and click “choice 1”, then his domicile and workplace position will display on the map, the best switch for him as well; it will also display the distance and duration for arriving at the new workplace.
Conclusion
In this blog, I talked about how to apply haversine distance and real distance
with haversine python module and Google Distance Matrix API. Hope it’s useful
for you.
Reference
- “Great-circle distance”, en.wikipedia.org. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great-circle_distance
- “Distance Matrix API”, developers.google.com. [Online]. Available: https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/distance-matrix/start
- 633839, “Bluff South Island New Zealand”, pixabay.com. [Online]. Available: https://pixabay.com/photos/bluff-south-island-new-zealand-2418709/